GoF. Паттерны проектирования
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Порождающие
паттерны
Abstract Factory
Предоставляет интерфейс для создания
семейств взаимосвязанных или взаимозависимых объектов, не специфицируя их
конкретных классов.

• AbstractFactory (ContinentFactory)
- declares an interface for operations that create abstract products
• ConcreteFactory (AfricaFactory, AmericaFactory)
- implements the operations to create concrete product objects
• AbstractProduct (Herbivore, Carnivore)
- declares an interface for a type of product object
• Product (Wildebeest, Lion, Bison, Wolf)
- defines a product object to be created by the corresponding concrete factory implements the AbstractProduct interface
• Client (AnimalWorld)
- uses interfaces declared by AbstractFactory and AbstractProduct classes
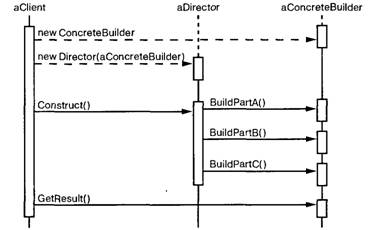
Builder
Отделяет конструирование сложного объекта
от его представления, так что в результате одного и того же процесса
конструирования могут получаться разные представления.

• Builder (VehicleBuilder)
- specifies an abstract interface for creating parts of a Product object
• ConcreteBuilder (MotorCycleBuilder, CarBuilder, ScooterBuilder)
- constructs and assembles parts of the product by implementing the Builder interface
- defines and keeps track of the representation it creates
- provides an interface for retrieving the product
• Director (Shop)
Factory Method (Virtual Constructor)
Определяет интерфейс для создания объекта,
но оставляет подклассам решение о том, какой класс инстанцировать.

• Product (Page)
- defines the interface of objects the factory method creates
• ConcreteProduct (SkillsPage, EducationPage, ExperiencePage)
- implements the Product interface
• Creator (Document)
- declares the factory method, which returns an object of type Product.
Creator may also define a default implementation of the factory method that returns a default ConcreteProduct object.
- may call the factory method to create a Product object.
• ConcreteCreator (Report, Resume)
- overrides the factory method to return an instance of a ConcreteProduct.
Prototype
Задает виды создаваемых объектов с помощью
экземпляра-прототипа и создает новые объекты путем копирования этого прототипа.

The classes and/or objects participating in this pattern are:
• Prototype (ColorPrototype)
- declares an interace for cloning itself
• ConcretePrototype (Color)
- implements an operation for cloning itself
• Client (ColorManager)
- creates a new object by asking a prototype to clone itself
Singleton
Гарантирует, что у класса есть только один
экземпляр, и предоставляет к нему глобальную точку доступа.

• Singleton (LoadBalancer)
- defines an Instance operation that lets clients access its unique instance. Instance is a class operation.
- responsible for creating and maintaining its own unique instance.
Структурные
паттерны
Adapter (Wrapper)
Преобразует интерфейс одного класса в
интерфейс другого, который ожидают клиенты. Адаптер обеспечивает совместную
работу классов с несовместимыми интерфейсами, которая без него была бы
невозможна.

• Target (ChemicalCompound)
- defines the domain-specific interface that Client uses.
• Adapter (Compound)
- adapts the interface Adaptee to the Target interface.
• Adaptee (ChemicalDatabank)
- defines an existing interface that needs adapting.
• Client (AdapterApp)
- collaborates with objects conforming to the Target interface.
Bridge
Отделить абстракцию от ее реализации так,
чтобы то и другое можно было изменять независимо.
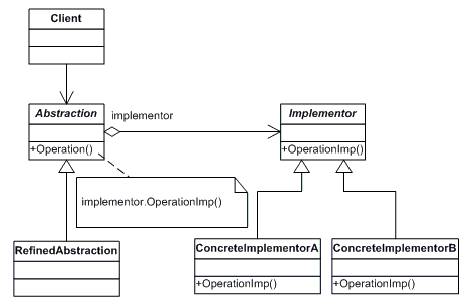
• Abstraction (BusinessObject)
- defines the abstraction's interface.
- maintains a reference to an object of type Implementor.
• RefinedAbstraction (CustomersBusinessObject)
- extends the interface defined by Abstraction.
• Implementor (DataObject)
- defines the interface for implementation classes. This interface doesn't have to correspond exactly to Abstraction's interface; in fact the two interfaces can be quite different. Typically the Implementation interface provides only primitive operations, and Abstraction defines higher-level operations based on these primitives.
• ConcreteImplementor (CustomersDataObject)
- implements the Implementor interface and defines its concrete implementation.

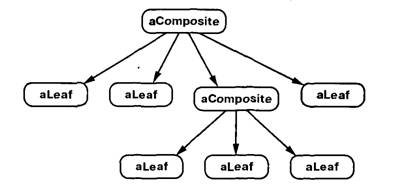
Composite
Компонует объекты в древовидные структуры для представления иерархий часть-целое. Позволяет клиентам единообразно трактовать индивидуальные и составные объекты.

• Component (DrawingElement)
- declares the interface for objects in the composition.
- implements default behavior for the interface common to all classes, as appropriate.
- declares an interface for accessing and managing its child components.
- (optional) defines an interface for accessing a component's parent in the recursive structure, and implements it if that's appropriate.
• Leaf (PrimitiveElement)
- represents leaf objects in the composition. A leaf has no children.
- defines behavior for primitive objects in the composition.
• Composite (CompositeElement)
- defines behavior for components having children.
- stores child components.
- implements child-related operations in the Component interface.
• Client (CompositeApp)
- manipulates objects in the composition through the Component interface.
Decorator (Wrapper)
Динамически добавляет объекту новые
обязанности. Является гибкой альтернативой порождению подклассов с целью
расширения функциональности.

• Component (LibraryItem)
- defines the interface for objects that can have responsibilities added to them dynamically.
• ConcreteComponent (Book, Video)
- defines an object to which additional responsibilities can be attached.
• Decorator (Decorator)
- maintains a reference to a Component object and defines an interface that conforms to Component's interface.
• ConcreteDecorator (Borrowable)
- adds responsibilities to the component.

Façade
Предоставляет унифицированный интерфейс
вместо набора интерфейсов некоторой подсистемы. Фасад определяет интерфейс
более высокого уровня, который упрощает использование подсистемы.

• Facade (MortgageApplication)
- knows which subsystem classes are responsible for a request.
- delegates client requests to appropriate subsystem objects.
• Subsystem classes (Bank, Credit, Loan)
- implement subsystem functionality.
- handle work assigned by the Facade object.
Flyweight
Использует разделение (sharing) для эффективной поддержки множества мелких объектов.

• Flyweight (Character)
- declares an interface through which flyweights can receive and act on extrinsic state.
• ConcreteFlyweight (CharacterA, CharacterB, ..., CharacterZ)
- implements the Flyweight interface and adds storage for intrinsic state, if any. A ConcreteFlyweight object must be sharable. Any state it stores must be intrinsic, that is, it must be independent of the ConcreteFlyweight object's context.
• UnsharedConcreteFlyweight ( not used )
- not all Flyweight subclasses need to be shared. The Flyweight interface enables sharing, but it doesn't enforce it. It is common for UnsharedConcreteFlyweight objects to have ConcreteFlyweight objects as children at some level in the flyweight object structure (as the Row and Column classes have).
• FlyweightFactory (CharacterFactory)
- creates and manages flyweight objects
- ensures that flyweight are shared properly. When a client requests a flyweight, the FlyweightFactory objects supplies an existing instance or creates one, if none exists.
• Client (FlyweightApp)
- maintains a reference to flyweight(s).
- computes or stores the extrinsic state of flyweight(s).
Приспособленец,
представляющий букву «а», содержит только соответсвующий ей код; ни положение,
ни шрифт буквы ему хранить не надо. Клиенты передают приспособленцу всю
зависящую от контекста информацию, которая нужна, чтобы он мог изобразить себя.

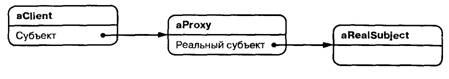
Proxy
Является суррогатом другого объекта и
контролирует доступ к нему.

• Proxy (MathProxy)
- maintains a reference that lets the proxy access the real subject. Proxy may refer to a Subject if the RealSubject and Subject interfaces are the same.
- provides an interface identical to Subject's so that a proxy can be substituted for the real subject.
- controls access to the real subject and may be responsible for creating and deleting it.
- other responsibilites depend on the kind of proxy:
- remote proxies are responsible for encoding a request and its arguments and for sending the encoded request to the real subject in a different address space.
- virtual proxies may cache additional information about the real subject so that they can postpone accessing it. For example, the ImageProxy from the Motivation caches the real images's extent.
- protection proxies check that the caller has the access permissions required to perform a request.
• Subject (IMath)
- defines the common interface for RealSubject and Proxy so that a Proxy can be used anywhere a RealSubject is expected.
• RealSubject (Math)
- defines the real object that the proxy represents.
Паттерны
поведения
Chain of Resposibility
Позволяет избежать привязки отправителя
запроса к его получателю, давая шанс обработать запрос нескольким объектам.
Свзязывает объекты-получатели в цепочку и передает запрос вдоль этой цепочки,
пока его не обработают.
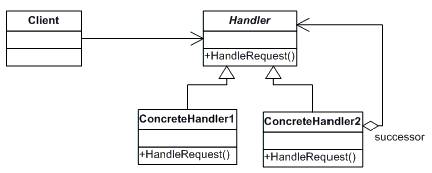
• Handler (Approver)
- defines an interface for handling the requests
- (optional) implements the successor link
• ConcreteHandler (Director, VicePresident, President)
- handles requests it is responsible for
- can access its successor
- if the ConcreteHandler can handle the request, it does so; otherwise it forwards the request to its successor
• Client (ChainApp)
- initiates the request to a ConcreteHandler object on the chain
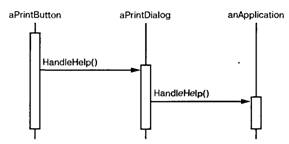

Command
Инкапсулирует запрос как объект, позволяя
тем самым задавать параметры клиентов для обработки соответствующих запросов,
ставить запросы в очередь или протоколировать из, а тажке поддерживать отмену
операций.

• Command (Command)
- declares an interface for executing an operation
• ConcreteCommand (CalculatorCommand)
- defines a binding between a Receiver object and an action
- implements Execute by invoking the corresponding operation(s) on Receiver
• Client (CommandApp)
- creates a ConcreteCommand object and sets its receiver
• Invoker (User)
- asks the command to carry out the request
• Receiver (Calculator)
- knows how to perform the operations associated with carrying out the request.

Interpreter
Для заданного языка
определяет представление его грамматики, а также интерпретатор предложений
этого языка.

• AbstractExpression (Expression)
- declares an interface for executing an operation
• TerminalExpression ( ThousandExpression, HundredExpression, TenExpression, OneExpression )
- implements an Interpret operation associated with terminal symbols in the grammar.
- an instance is required for every terminal symbol in the sentence.
• NonterminalExpression ( not used )
- one such class is required for every rule R ::= R1R2...Rn in the grammar
- maintains instance variables of type AbstractExpression for each of the symbols R1 through Rn.
- implements an Interpret operation for nonterminal symbols in the grammar. Interpret typically calls itself recursively on the variables representing R1 through Rn.
• Context (Context)
- contains information that is global to the interpreter
• Client (InterpreterApp)
- builds (or is given) an abstract syntax tree representing a particular sentence in the language that the grammar defines. The abstract syntax tree is assembled from instances of the NonterminalExpression and TerminalExpression classes
- invokes the Interpret operation
Iterator (Cursor)
Предоставляет способ последовательного доступа ко всем
элементам составного объекта, не раскрывая его внутреннего представления.

• Iterator (AbstractIterator)
- defines an interface for accessing and traversing elements.
• ConcreteIterator (Iterator)
- implements the Iterator interface.
- keeps track of the current position in the traversal of the aggregate.
• Aggregate (AbstractCollection)
- defines an interface for creating an Iterator object
• ConcreteAggregate (Collection)
- implements the Iterator creation interface to return an instance of the proper ConcreteIterator
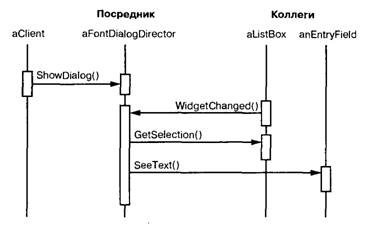
Mediator
Определяет объект, инкапсулирующий способ
взаимодействия множества объектов. Посредник обеспечивает слабую связанность
системы, избавляя объекты от необходимости явно ссылаться друг на друга и
позволяя тем самым независимо изменять взаимодействия между ними.
Посредник отвечает за координацию взаимодействий между группой объектов. Он
избавляет вхоящие в группу объекты от необходимости явно ссылаться друг на
друга.

• Mediator (IChatroom)
- defines an interface for communicating with Colleague objects
• ConcreteMediator (Chatroom)
- implements cooperative behavior by coordinating Colleague objects
- knows and maintains its colleagues
• Colleague classes (Participant)
- each Colleague class knows its Mediator object
- each colleague communicates with its mediator whenever it would have otherwise communicated with another colleague

Memento
Не нарушая инкапсуляции, фиксирует и
выносит за пределы объекта его внутреннее состояние так, чтобы поздее можно
было восстановить в нем объект.

• Memento (Memento)
- stores internal state of the Originator object. The memento may store as much or as little of the originator's internal state as necessary at its originator's discretion.
- protect against access by objects of other than the originator. Mementos have effectively two interfaces. Caretaker sees a narrow interface to the Memento -- it can only pass the memento to the other objects. Originator, in contrast, sees a wide interface, one that lets it access all the data necessary to restore itself to its previous state. Ideally, only the originator that produces the memento would be permitted to access the memento's internal state.
• Originator (SalesProspect)
- creates a memento containing a snapshot of its current internal state.
- uses the memento to restore its internal state
• Caretaker (Caretaker)
- is responsible for the memento's safekeeping
- never operates on or examines the contents of a memento.

Observer
Определяет зависимость типа «один ко
многим» между объектами таким образом, что при изменении состояния одного
объекта все зависящие от него оповещаются об этом и автоматически обновляются.
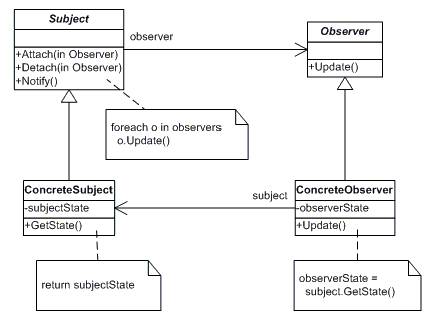
• Subject (Stock)
- knows its observers. Any number of Observer objects may observe a subject
- provides an interface for attaching and detaching Observer objects.
• ConcreteSubject (IBM)
- stores state of interest to ConcreteObserver
- sends a notification to its observers when its state changes
• Observer (IInvestor)
- defines an updating interface for objects that should be notified of changes in a subject.
• ConcreteObserver (Investor)
- maintains a reference to a ConcreteSubject object
- stores state that should stay consistent with the subject's
- implements the Observer updating interface to keep its state consistent with the subject's

State
Позволяет объекту варьировать свое поведение в зависимости от внутреннего состояния. Извне создается впечатление, что изменился класс объекта.

• Context (Account)
- defines the interface of interest to clients
- maintains an instance of a ConcreteState subclass that defines the current state.
• State (State)
- defines an interface for encapsulating the behavior associated with a particular state of the Context.
• Concrete State (RedState, SilverState, GoldState)
- each subclass implements a behavior associated with a state of Context

Strategy (Policy)
Определяет семейство алгоритмов, инкапсулирует каждый из них и делает их взаимозаменяемыми. Стратегия позволяет изменять алгоритмы независимо от клиентов, которые ими пользуются.

• Strategy (SortStrategy)
- declares an interface common to all supported algorithms. Context uses this interface to call the algorithm defined by a ConcreteStrategy
• ConcreteStrategy (QuickSort, ShellSort, MergeSort)
- implements the algorithm using the Strategy interface
• Context (SortedList)
- is configured with a ConcreteStrategy object
- maintains a reference to a Strategy object
- may define an interface that lets Strategy access its data.
Template Method
Шаблонный метод определяет основу алгоритма и позволяет подклассам переопределить некоторые шаги алгоритма, не изменяя его структуру в целом.

• AbstractClass (DataObject)
- defines abstract primitive operations that concrete subclasses define to implement steps of an algorithm
- implements a template method defining the skeleton of an algorithm. The template method calls primitive operations as well as operations defined in AbstractClass or those of other objects.
• ConcreteClass (CustomerDataObject)
- implements the primitive operations of carry out subclass-specific steps of the algorithm
Visitor
Описывает операцию, выполняемую с каждым объектом из некоторой структуры. Паттерн посетитель позволяет определить новую операцию, не изменяя классы этих объектов.

• Visitor (Visitor)
- declares a Visit operation for each class of ConcreteElement in the object structure. The operation's name and signature identifies the class that sends the Visit request to the visitor. That lets the visitor determine the concrete class of the element being visited. Then the visitor can access the elements directly through its particular interface
• ConcreteVisitor (IncomeVisitor, VacationVisitor)
- implements each operation declared by Visitor. Each operation implements a fragment of the algorithm defined for the corresponding class or object in the structure. ConcreteVisitor provides the context for the algorithm and stores its local state. This state often accumulates results during the traversal of the structure.
• Element (Element)
- defines an Accept operation that takes a visitor as an argument.
• ConcreteElement (Employee)
- implements an Accept operation that takes a visitor as an argument
• ObjectStructure (Employees)
- can enumerate its elements
- may provide a high-level interface to allow the visitor to visit its elements
- may either be a Composite (pattern) or a collection such as a list or a set
